Roof Solar Electricity
Solar panels producing a warm air flow could be placed on the roof of a house. The air current could drive a convector generator producing electricity:
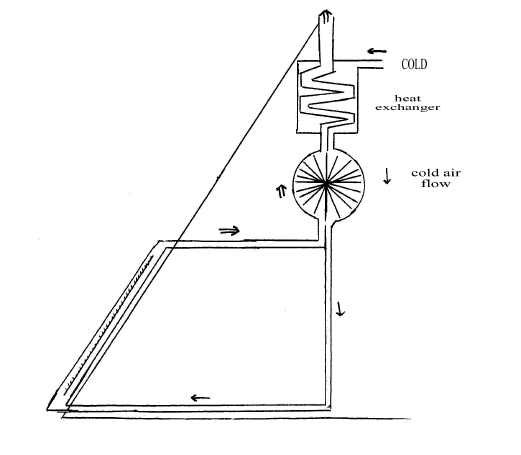
The solar panel covers the lower half of the South facing roof. As solar energy is absorbed, warm air will rise to drive the generator. Any residual energy is absorbed by incoming cold air in the heat exchanger. The cold air down flow also drives the generator as it flows down to enter the panel at its lowest point. The generator and heat exchanger would fit into the attic roof space. There would need to be some difference in level between the cold air intake and the mouth of the warm air leaving of perhaps up to 1 metre to drive the system. With a well insulated solar panel, an efficient heat exchanger and convector generator, there should be minimal energy loss. The conversion of solar energy into electricity with 80% efficiency should be possible.
A small house will have a floor area of 40 square metres. Incident solar energy at Aberporth averages 600 kWh/sq metre/year. If one half of the South facing roof has panels installed, an efficiency of 80% generation would produce 4800 units of electricity annually. This is higher than domestic demand.
The same principles could apply to provide solar electricity for schools, hospitals, offices and factories. Indeed the South facing wall and/or adjacent land could be used for solar panel area.
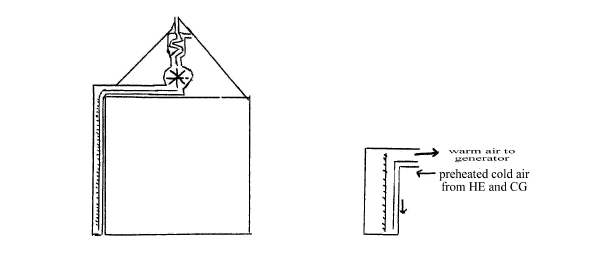
In the sketch as drawn electricity generation could be on the floor of the roof space. If the panels were placed on land adjacent to the building, they could be placed at optimal angle for maximum solar energy or indeed track the sun. All of the above involves materials that are far cheaper than for photovoltaics and generation of electricity should be far more efficient.